Catalyst Biology Cell . like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells: the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter kcat/km. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or consumed in the reaction. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that.
from biotechnologymcq.com
like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or consumed in the reaction. These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells: the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter kcat/km.
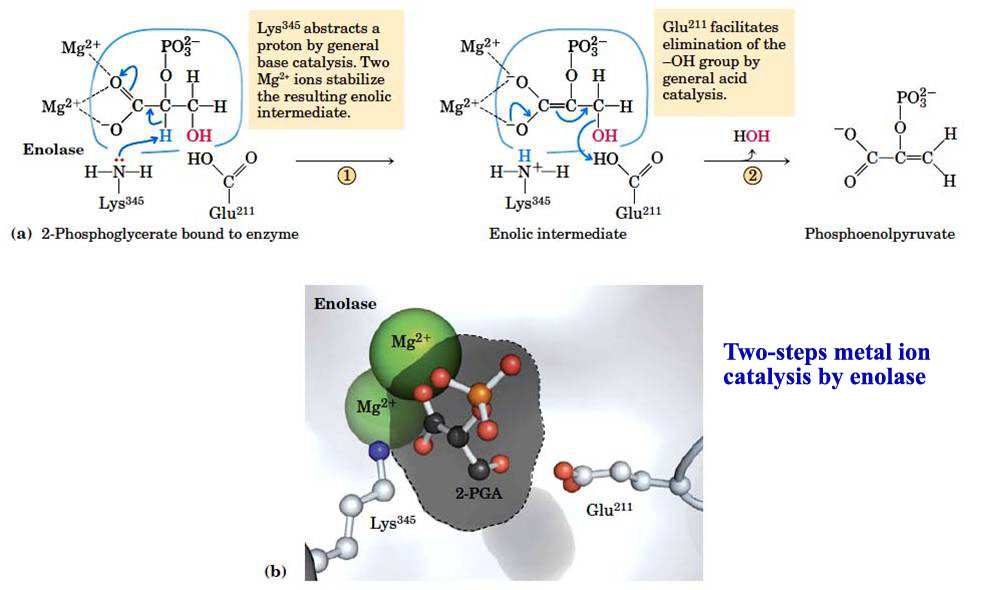
Enzyme V(II) Catalytic Mechanisms II Metal Ion catalysis; Catalysis by
Catalyst Biology Cell enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or consumed in the reaction. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter kcat/km. two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells:
From slideplayer.com
Biological catalysts Enzymes IGCSE Biology. ppt download Catalyst Biology Cell two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells: an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or consumed in the reaction. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Catalysts PowerPoint Presentation ID2683737 Catalyst Biology Cell Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter kcat/km. These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. a fundamental task of proteins is. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzymes as Biological Catalysts PowerPoint Presentation, free Catalyst Biology Cell enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells: like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From exozpzccv.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Biology Simple Definition at Lydia Hatcher blog Catalyst Biology Cell describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or consumed in the reaction. two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells: the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From www.researchgate.net
The MHETase wholecell catalyst concept. A The MHETase wholecell Catalyst Biology Cell in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter kcat/km. like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From biotechnologymcq.com
Enzyme V(II) Catalytic Mechanisms II Metal Ion catalysis; Catalysis by Catalyst Biology Cell enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells: a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter kcat/km. in. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From pubs.acs.org
StateoftheArt Biocatalysis ACS Central Science Catalyst Biology Cell like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells: describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that.. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From exowzdqkr.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Biology Image at Anna Schofield blog Catalyst Biology Cell a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or consumed in the reaction. enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. in this chapter, we look. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From cekrvawv.blob.core.windows.net
Enzymes A Level Chemistry at Mark Ryan blog Catalyst Biology Cell a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or consumed in the reaction. in. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From www.dreamstime.com
Catalyst Surface with Catalytic Reaction Stock Vector Illustration of Catalyst Biology Cell a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells: These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. describe the role of enzymes. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From exozpzccv.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Biology Simple Definition at Lydia Hatcher blog Catalyst Biology Cell like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter kcat/km. enzymes. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From www.researchgate.net
a Schematic representation of wholecell catalytic reaction system for Catalyst Biology Cell a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter kcat/km. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. describe the role. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From www.researchgate.net
Catalytic processes on a solid catalyst. Download Scientific Diagram Catalyst Biology Cell Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From www.scribd.com
Essential Cell Biology Energy, Catalysis and Biosynthesis PDF Catalyst Biology Cell two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells: Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From cemwppzp.blob.core.windows.net
What Are Catalysts In Biology at Marguerite Wiliams blog Catalyst Biology Cell Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts. These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From exowzdqkr.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Biology Image at Anna Schofield blog Catalyst Biology Cell These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter kcat/km. describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms. like the laboratory catalysts,. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From www.creative-enzymes.com
Whole Cell Biocatalysts Catalyst Biology Cell These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. in this chapter, we look at the properties and mechanism of action of enzymes. describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways. like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions. Catalyst Biology Cell.
From www.chemistryviews.org
SolarPowered WholeCell P450 Catalysis ChemistryViews Catalyst Biology Cell like the laboratory catalysts, enzymes frequently have activators—coenzymes, which may be. two opposing streams of chemical reactions occur in cells: These include allosteric change (induced fit, enzyme regulation), energetic events. the catalytic efficiency (proficiency, specificity) of an enzyme (or any catalyst) is given by the kinetic parameter kcat/km. an enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance. Catalyst Biology Cell.